Investment portfolios typically seek to maximize overall returns, with individual choices on how to utilize those returns varying among investors.
The most effective way to guarantee that you are developing a successful portfolio is by conducting regular evaluations.
It is beneficial for investors seeking consistent performance, less volatility, and lower risk to understand how to determine the actual returns of an investment.
Investors frequently focus on returns and earnings without considering the effects of inflation.
The actual return of an investment takes into account inflation and provides a more precise indication of the profit or loss.
The return of an asset is the percentage increase in value compared to the original cost, not accounting for inflation.
The revenue generated by an asset is distinct in that it represents the earnings, like dividends, received from an asset in comparison to its initial price. Unlike income calculations, return calculations take into account capital gains.
We will gain a deeper understanding of investments with actual returns, how to measure them, and the significance of seeking them out when investing. Happy reading!
What is actual yield and how does inflation impact its computation?
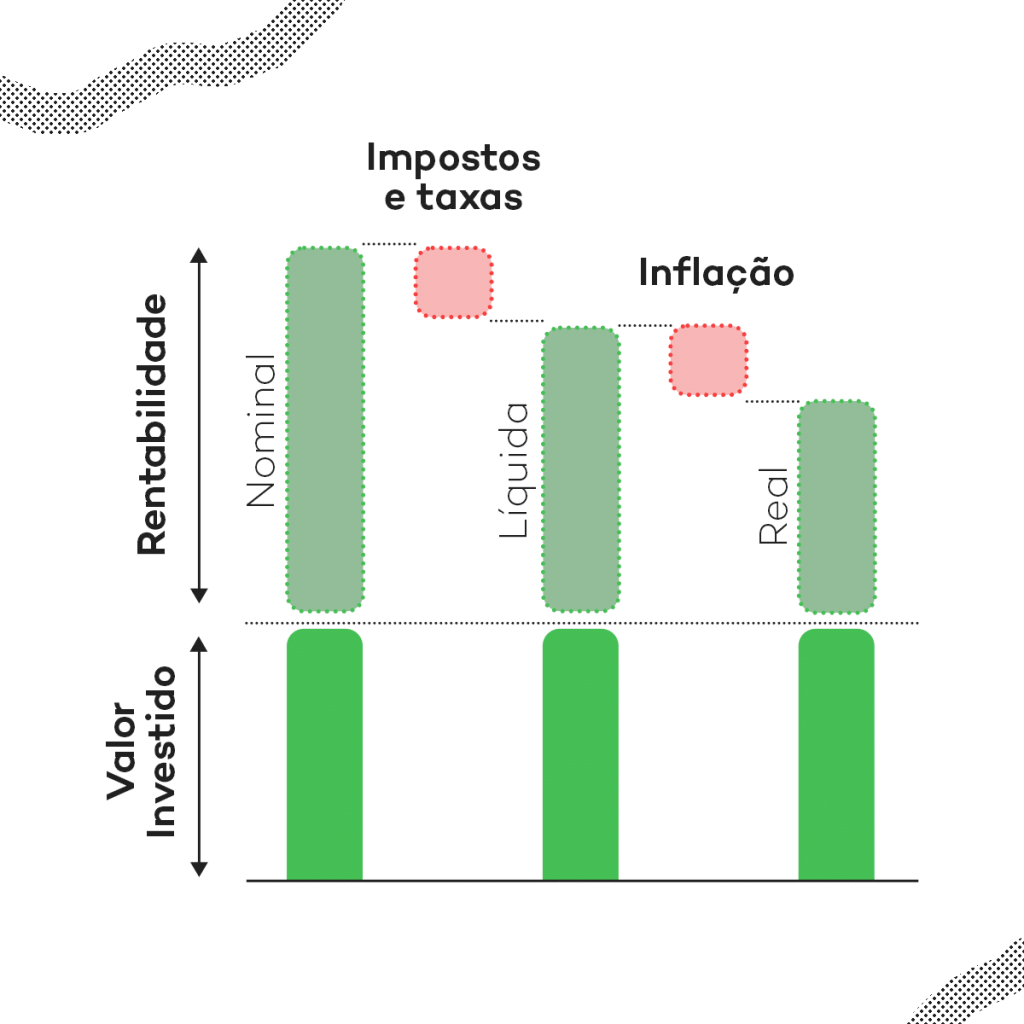
A true return is the profit earned from an investment after considering taxes and inflation.
A real return rate refers to the yearly percentage return on an investment, accounting for adjustments in prices resulting from inflation or external factors.
This approach presents the nominal return rate adjusted for inflation to ensure that the constant capital retains its purchasing power.
chsyys/StockVault
Inflation refers to a rise in prices for goods and services over time, leading to a decrease in purchasing power as you end up paying more for the same products.
Three years ago, you purchased one kilogram of sugar for $5. Today, the same quantity of sugar costs $12.
Your investment should keep pace with inflation to avoid losing returns. If your investments grow by 2% annually, but inflation rises by 3% each year, you effectively lose all your returns.
As an investor, it’s important to take into account the real return, which is adjusted for inflation and factors in the Consumer Price Index (IPCA), expenses, and taxes.
Investors often prioritize real incomes and real returns when making investment decisions, although security can sometimes outweigh the importance of higher returns.
When investing, one should consider administration, custody costs, income tax, and inflation to avoid negative income.
What is the significance of negative profitability?
Negative profitability occurs when the actual income from an investment is the same as or lower than the inflation rate.
Investors should consider more than just the actual returns when making investment decisions. Other factors to focus on include long-term objectives, investment timeline, and risk tolerance.
It is crucial to understand how inflation is affecting the returns on investments in every situation.
Make sure to focus on your actual return and income rather than just looking at the nominal return or yield when assessing an investment. This approach will lead to achieving favorable yields.
What is the primary advantage of actual profitability?
The real return rate accounts for inflation and provides a more precise evaluation of investment performance compared to the nominal return rate.
Nominal returns exceed actual returns, except during periods of inflation or zero deflation.
It shows investors how their investments are doing compared to inflation over a specific time frame, allowing them to determine if their purchasing power has gone up or down.
If your investment earns the same as inflation, your purchasing power remains unchanged. But if it earns less than inflation, you lose purchasing power.
Explore and appreciate the distinction between revenue and profitability here.
What sets real profitability apart from nominal profitability?
We need to utilize nominal profitability to determine the actual profitability.
The nominal return profitability is the return rate without considering inflation adjustments.
Nominal profitability is typically higher than real return profitability, except during deflation periods, also known as negative inflation.
During periods of very high inflation, the apparent profitability of nominal returns may increase, making investments appear more appealing.
A high inflation rate can lead to lower actual profits and potential losses for the investment.
The interest rate displayed in typical investment products is known as nominal return, and it is crucial to comprehend its benefits.
Real profitability will offer a more comprehensive understanding of the actual performance of an investment.
Calculating actual profitability can be determined how?
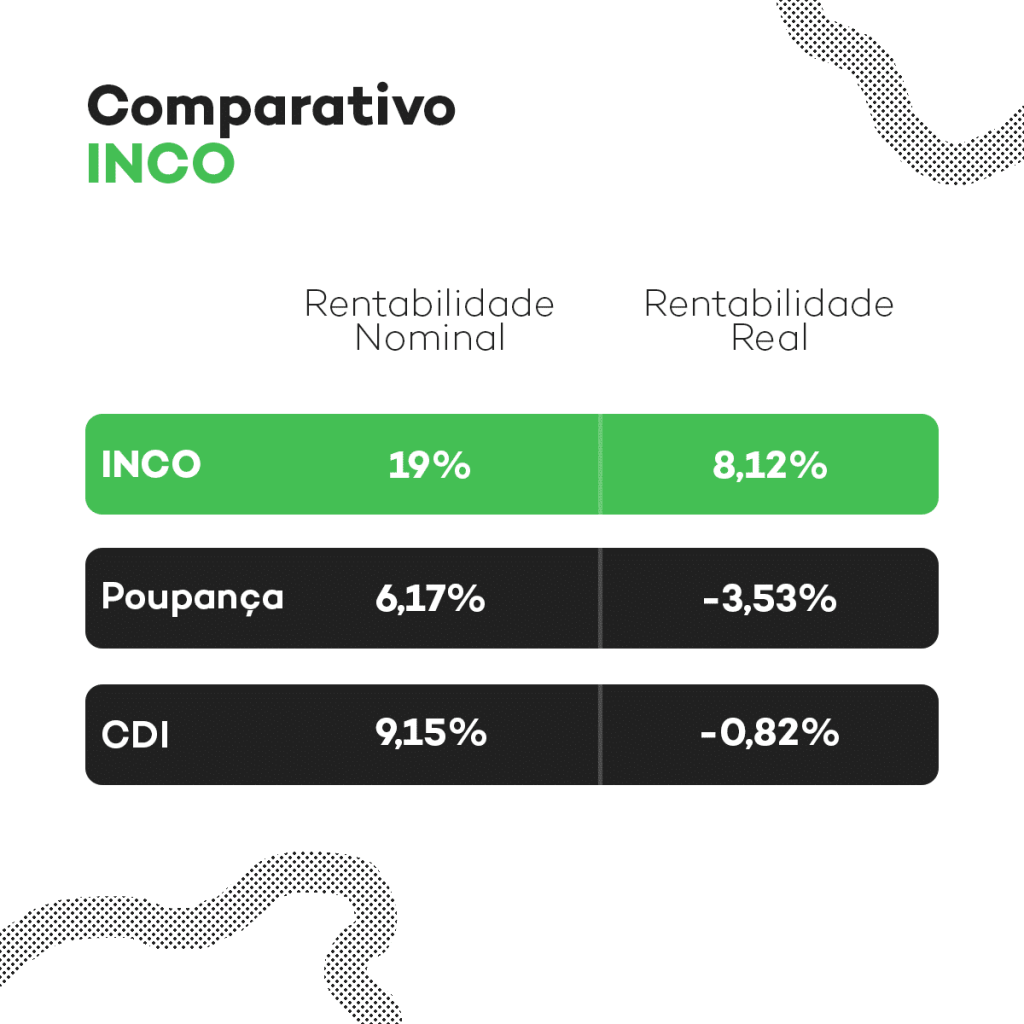
Calculating actual profitability is straightforward – simply deduct the current inflation rate percentage.
You should utilize the formula provided for this purpose.
The formula is calculated as: r = (1 + income) ÷ (1 + inflation) – 1.
Let’s consider a real-life example:
If you invested in a fixed income asset that earned 8% in a year while inflation was 4% during that time.
To perform the calculation, start by converting the percentage figures to decimals by dividing by 100. Next, multiply the assigned value of each asset by its earnings during the timeframe.
Using the formula yields:
The formula can be simplified as (1 + 0.08) divided by (1 + 0.04) minus 1.
The outcome is the actual profit margin, which stands at 3.8%.
Investors often discover that the application’s profitability is around 8% during a certain period. However, it’s crucial to factor in inflation to determine the real profitability.
Diversifying your investments ensures financial gains.
Investing in a diverse range of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and funds is definitely a wise decision.
Different types of assets respond distinctively to global events and market influences, making a diversified portfolio less susceptible to risks.
Investing sooner can lead to extended investment returns due to the passage of time.
Composite interest happens when interest is earned on both the initial investment and the returns already made by that investment.
Having a varied investment portfolio with a focus on long-term goals is typically viewed as the most effective approach to optimizing returns.
To achieve a favorable investment return, investors need to consider their objectives, understand the actual returns, assess risks, and determine their investment profile.
Consider your investment objectives, begin at an early stage, and spread out your investments. INCO is here to assist you in making prudent investment decisions and working toward your goals.
In conclusion
An investor’s primary objective is to generate profits. Although it’s impossible to foresee the exact outcome of your investment portfolio, there are various measures available to help determine a practical projection of your portfolio’s future expansion.
It is crucial to take into account actual profitability when deciding to invest.










Comments