An investor who comprehends the interest curve and the fluctuations in the financial market has an advantage when it comes to investments.
Understanding the concept of the interest curve helps investors to consider the potential earnings when investing their money.
We have created a comprehensive guide in the upcoming article to help you grasp the role of the curve, its impact on investments, and other related aspects.
What does the term interest curve refer to?
The interest curve is simply a visual depiction of the anticipated interest rates in the future market.
Data gathered from government and corporate debt securities with varying maturity dates and interest rates form the basis for the interest curve, which is constructed by connecting these data points on a chart.
The interest curve reflects market agents’ predictions of interest rates over a specific period using available political, economic, monetary, and social information.
The interest curve in investments displays the expected earnings a lender anticipates when lending money for a specific duration.
Why does the interest curve matter?
Investors’ expectations on a country’s interest rates are reflected in the yield curve, serving as a gauge for fixed-income investments and future interest rate trends.
We can determine the value of switching to variable income investments like government bonds by analyzing the interest curve and considering the anticipated decrease in interest rates.
People looking to start a business often rely on this concept as well, as it is illogical to take on risky investments that offer the same or lower returns than a federal investment during the same timeframe.
What types of interest rate curves exist?
Investors can analyze various graphical representations of interest curves to assess their average return expectations depending on their shape.
This article will cover five categories: regular, steep, upside-down, level, and mixed.
Standard interest curve
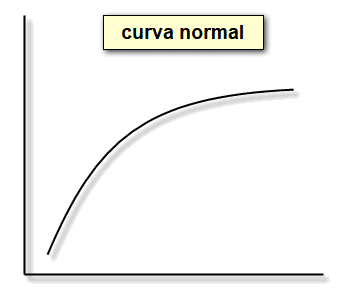
The curved line is depicted as slightly concave, indicating a positive interpretation.
Little inflationary pressure is anticipated, which is not negative, and economic actors are being regulated, according to his analysis.
Economic growth is anticipated to boost as the curve inclines, leading to heightened pressure on rates and potential government intervention.
sharp incline in interest rates
Also referred to as “strongly tilted,” it can indicate two distinct scenarios.
The economy may be moving into a phase of favorable growth opportunities.
The government is having difficulty funding its long-term deficit.
Economic growth periods are closely connected to inflationary pressures, resulting in a steep curve. This situation typically prompts a more assertive government response in terms of monetary policy, which involves increasing interest rates to manage inflation.
Investors feel insecure about making long-term commitments and may seek government compensation when faced with challenges in financing deficits.
Interest curve that is inverted
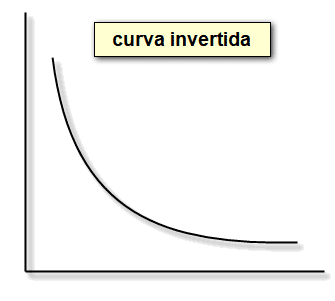
A typical yield curve is characterized by a gradual upward slope that is slightly concave, indicating improved economic conditions.
When it inverts, it indicates that short-term interest rates are greater than long-term rates.
This rare curve typically triggers movement in the financial market as it signals an economic downturn.
This suggests that economic actors are indicating a potential economic decline or stagnation, putting pressure on the government to reduce interest rates in an effort to revitalize and advance the economy.
This is typically the most unfavorable financial situation for the economy, leading investors to buy long-term securities to safeguard their returns against potential interest rate cuts by the government.
Interest curve that is flat
A flat interest curve is a direct line where short and long-term interest rates are the same or very similar.
A flat curve may suggest a period of uncertainty when economic entities struggle within a setting of recession or inflation, leading to indecisiveness in the economy.
A flat curve may also signify a period of change.
Hybrid or non-traditional interest rate curve
Interest curves are not limited to just basic and preset curves; hybrid curves can also be present.
These curves depict varying long and short-term projections, creating unique patterns with diverse geometric qualities. This situation is likely to give rise to numerous potential outcomes.
To understand hybrid curves, it is important to closely examine their depiction as they combine multiple meanings and blend fundamental concepts from other curves.
How is the interest curve determined?
Now that you have a better grasp of the idea, you may be curious about how to determine the interest curve.
You don’t have to worry about learning how to do these calculations to enhance your investment quality.
The ANBIMA calculates and shares interest curves for a specific period on its website for public access.
What factors impact the behavior of interest rates over time?
Three primary elements can impact the behavior of interest curves.
Inflation refers to the increase in prices.
Inflationary pressure has a direct impact on the upward-sloping interest curve displayed in a chart.
Economic expansion
During times of economic expansion, rising inflation and government-imposed interest rate hikes cause a steep interest rate curve.
Interest rate
High interest in future contracts, known as the “openness” of the curve, has a direct impact on the economic market.
This introduction enhances the investment’s return appeal but lowers the prices of securities for previous buyers.
If the interest rate decreases, short-term securities become more valuable, causing the yield curve to “flatten” further.
How does the yield curve affect your investment?
Investors may encounter the risk of yield curve inversion, where long-term interest rates fall below short-term rates.
Investors also face the risk of their returns fluctuating with changes in interest rates.
When interest rates decrease, investors may experience a reduction in earnings due to lower return rates.
Investors need to evaluate the interest rate curve risk when investing in fixed income, as it also indicates future economic growth when it decreases.
Interest curves and economic growth are closely related over time.
Investors in public bonds like direct treasury or private securities tied to inflation, such as real estate funds, debentures, CDBs, LCIs, and LCAs, must monitor the nation’s interest rates carefully.
By comprehending how it works and is interpreted, one can utilize the yield curve to assess the direction of investments.
Using the interest curve to your advantage in investment.
It is beneficial to understand how to benefit from or safeguard against the impact of changes in the interest curve on investments.
Projections seen in interest rate trends can provide valuable guidance to investors when making decisions. For instance, a closing curve suggesting a future decrease in interest rates could signal opportunities to invest in fixed securities.
Before the curve begins, it might be beneficial to consider post-fixed titles in order to capitalize on the high interest.
If you already have an investment portfolio, understanding the curve can assist in identifying investments for protection.
When discussing protective measures in the financial market, it is important to highlight the significance of diversification. This involves spreading investments across various types of assets that are not closely related, which helps to reduce risks and enhance the growth potential of your portfolio.
In conclusion
If you are interested in investments, one crucial concept to examine is the interest curve.
It can be very beneficial for making investment decisions and managing an investment portfolio by ensuring alignment with economic trends and strategies.
It is a tool for investing that should be utilized alongside other tools to assess a potential investment opportunity.
Understanding how interest rates change in a particular time frame empowers you to make informed financial decisions and recognize and seize the top investment prospects.








Comments